Error java java lang exceptionininitializererror
Ошибка: Exception in thread «main» java
Если вы сталкивались с ошибками Exception in thread «main», то в этой статье я расскажу что это значит и как исправить ее на примерах.
При работе в среде Java, типа Eclipse или Netbeans, для запуска java-программы, пользователь может не столкнуться с этой проблемой, потому что в этих средах предусмотрен качественный запуск с правильным синтаксисом и правильной командой.
Здесь мы рассмотрим несколько общих java-исключений(Exceptions) в основных исключениях потоков, которые вы можете наблюдать при запуске java-программы с терминала.

Исключение в потоке java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError
Это исключение происходит, когда ваш класс java компилируется из другой версии JDK и вы пытаетесь запустить его из другой версии java. Рассмотрим это на простом примере:
Когда создаётся проект в Eclipse, он поддерживает версию JRE, как в Java 7, но установлен терминал Jawa 1.6. Из-за настройки Eclipse IDE JDK, созданный файл класса компилируется с Java 1.7.
Теперь при попытке запустить эту версию с терминала, программа выдает следующее сообщение исключения.
Если запустить версию Java1.7, то это исключение не появится. Смысл этого исключения – это невозможность компилирования java-файла с более свежей версии на устаревшей версии JRE.
Исключение java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError
Существует два варианта. Первый из них – когда программист предоставляет полное имя класса, помня, что при запуске Java программы, нужно просто дать имя класса, а не расширение.
Обратите внимание: если написать: .class в следующую команду для запуска программы — это вызовет ошибку NoClassDefFoundError. Причина этой ошибки — когда не удается найти файл класса для выполнения Java.
Второй тип исключения происходит, когда Класс не найден.
Обратите внимание, что класс ExceptionInMain находится в пакете com.journaldev.util, так что, когда Eclipse компилирует этот класс, он размещается внутри /com/journaldev/util. Следовательно: класс не найден. Появится сообщение об ошибке.
Исключение java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: main
Это исключение происходит, когда вы пытаетесь запустить класс, который не имеет метод main. В Java.7, чтобы сделать его более ясным, изменяется сообщение об ошибке:
Всякий раз, когда происходит исключение из метода main — программа выводит это исключение на консоль.
В первой части сообщения поясняется, что это исключение из метода main, вторая часть сообщения указывает имя класса и затем, после двоеточия, она выводит повторно сообщение об исключении.
Например, если изменить первоначальный класс появится сообщение System.out.println(10/0) ; Программа укажет на арифметическое исключение.
Методы устранения исключений в thread main
Выше приведены некоторые из распространенных исключений Java в потоке main, когда вы сталкиваетесь с одной из следующих проверок:
- Эта же версия JRE используется для компиляции и запуска Java-программы.
- Вы запускаете Java-класс из каталога классов, а пакет предоставляется как каталог.
- Ваш путь к классу Java установлен правильно, чтобы включить все классы зависимостей.
- Вы используете только имя файла без расширения .class при запуске.
- Синтаксис основного метода класса Java правильный.
Средняя оценка / 5. Количество голосов:
Спасибо, помогите другим — напишите комментарий, добавьте информации к статье.
Или поделись статьей
Видим, что вы не нашли ответ на свой вопрос.
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError in Java Program
JVM throws java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError , when there is an Exception ins >ExceptionInInitializerError in Java. This could be any exception e.g. java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBound or java.lang.NullPointerException . Java developers often confused with this error because, they think that they have not defined any static initializer block, then how come they are getting ExceptionInInitializerError; well, by default Java combines all static variable initialization inside a static initializer block and initialize them in the order they are declared in source file.
If suppose a variable ABC is declared at line 1, used at line 2 but initialized at line 3, then code at line 2 will throw java.lang.NullPointerException , which will be wrapped by JVM in ExceptionInInitializerError , and if that code happens to be executed by main thread then you will see «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError» in your console or log file.
In a large application with huge log files sometime this error got unnoticed, and programmers get alerted by dreaded java.lang.No >ExceptionInInitializerError . Since >NoClassDefFoundError .
In this article, we will see an example code, which generates exception during static initialization and results in «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError» . In later part, we will see how to fix this error.
Cause of «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError»
As with any other error or exception, by first looking at this line, you know that exception is java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError , which comes because of failure during >java command at command line or same >public static void main(String args[]) method. Now if you look at full stacktrace carefully, you don’t need to do anything because JVM prints name of the >ExceptionInInitializerError . It’s also a sub >LinkageError , which means if this error has occurred then you class will not be loaded into JVM memory. Now let’s take a look at our example program, which upon execution, throwing following error :
By looking at this stack trace, we know that actual error is java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException , which came at line 12 of StaticInitiazerDemo >get() method of ArrayList with index 0 and come because size of ArrayList was also zero (Index: 0, Size: 0 part of stack-trace). Now by following this information, you know that our List is empty, when we try to get first CreditCard from this list.
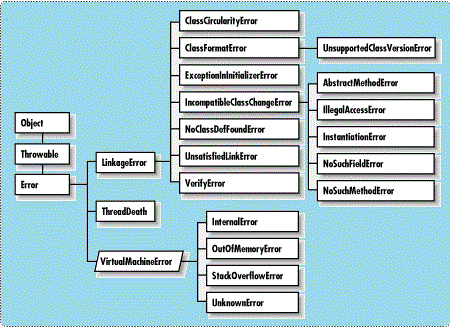
Here is class hierarchy of all Error class in Java. You can see that ExceptionInInitializerError inherit from LinkageError. Its also worth knowing that like RuntimeException, Errors are also unchecked and compiler doesn’t check for mandatory error handling code.
Things to remember:
1) Remember «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError» means Exception has occurred in main thread, and it is java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError , which is sub- >LinkageError and comes when JVM tries to load a >RuntimeException in static initializer block e.g. IndexOutOfBoundsException or NullPointerException.
2) Remember that JVM combines all static variable initialization into one static initializer block in the order they appear in source file. So, don’t think that absence of explicit static initializer block will not cause this error. In fact, you must ensure correct order of static variables i.e. if one variable initialization uses another variable then make sure that is initialized first.
4) Remember Static initializer block can throw RuntimeException but not checked Exception, because later required mandatory catch block for handling.
Java Exception Handling – ExceptionInInitializerError
Moving along through our in-depth Java Exception Handling series, today we’ll dive into the ExceptionInInitializerError, which is thrown when an error occurs within the static initializer of a class or object. Since an ExceptionInInitializerError isn’t ever the cause of a thrown error, catching such an exception provides an underlying causal exception that indicates what the actual source of the issue was.
Throughout this article we’ll examine the ExceptionInInitializerError by looking at where it resides in the overall Java Exception Hierarchy. We’ll then explore a simple and fully-functional code sample that illustrates how a static initializer works, and what might lead to a thrown ExceptionInInitializerError in such an initializer, so let’s get to it!
The Technical Rundown
All Java errors implement the java.lang.Throwable interface, or are extended from another inherited class therein. The full exception hierarchy of this error is:
Full Code Sample
Below is the full code sample we’ll be using in this article. It can be copied and pasted if you’d like to play with the code yourself and see how everything works.
When Should You Use It?
Since the appearance of an ExceptionInInitializerError indicates a problem within a static initializer , we should briefly examine what a static initializer is and how they’re typically used. Put simply, a static initializer block is a normal code block that is executed when the class is loaded.
A static initializer is created by enclosing code anywhere inside a class definition surrounded by braces ( < & >) and also preceded by the static keyword. For example:
As you can see in the code above, there can be as many static initializer blocks as desired within a class definition. Each will be executed in a top-down manner when the class is first loaded.
Static initializers are not to be confused with instance initializers (or instance members ), which are executed when the class is instantiated (i.e. a new object of that class type is created). Instance initializers are also executed just before the constructor method.
An instance initializer is written inside a class definition using two braces ( < & >), but without a preceding static keyword:
Just as with static versions, multiple instance initializers can be defined and will be executed from top to bottom.
The purpose of a static initializer is typically to execute any initialization code that must occur before a class can be used. Critically, static initializers are only executed once ever, the first time that class is loaded. Thus, they are great for classes that are frequently used throughout the application, but only need some basic configuration code to be executed once before multiple instances are used elsewhere, such as a database connection class.
To test a static initializer in “real” code we’ve added a simple snippet and field to our trusty Book class:
A static initializer block has been added near to the top of the class definition, and merely attempts to ensure the publicationType static field is an upper case value:
With this static initializer in place let’s try creating a new Book instance:
Executing this main(String[] args) method produces the following output:
Sure enough, this threw an ExceptionInInitializerError at us. Just as importantly, since ExceptionInInitializerErrors aren’t ever going to cause a problem themselves, catching such an exception always contains an actual causal exception , which is the error that was thrown within a static initializer that led to the caught ExceptionInInitializerError . In this case, we see the cause was a NullPointerException . With a bit of digging and consideration, we can see that the problem is within the static initializer code inside the Book class. It attempts to get the static publicationType value, but we don’t explicitly set an initial value for this field, so calling this references a null value, hence the NullPointerException . The solution is to either set an initial value for publicationType , or to include a try-catch block within the static initializer. In this case, a try-catch block handles the error, but doesn’t resolve the root cause, so it’s probably better to specify a default value instead:
Now, rerunning the same main(String[] args) method instantiates our Book just fine and outputs the results:
A few things worth noting. First, since our code to force the publicationType value to be upper case occurs within a static initializer, this occurs before our Book instance is initialized, as well as before the Book(String title, String author, Integer pageCount, Date publishedAt, String publicationType) constructor method is executed. Thus, even though we successfully change the publicationType from the default of Book to novel , it won’t be upper case’d unless we do so inside an instance or member initializer .
Additionally, since publicationType is a static field, this means it is unique to the entire Book class. If we were to create a second Book instance with a publicationType specified in the constructor of poem , the publicationType of our Game of Thrones Book instance would also have its publicationType changed to poem :
This code produces the following output:
As we can see, the publicationType of both instances is now the new value of poem , so just be ware that static members and initializers are global to all instances of a particular class.
The Airbrake-Java library provides real-time error monitoring and automatic exception reporting for all your Java-based projects. Tight integration with Airbrake’s state of the art web dashboard ensures that Airbrake-Java gives you round-the-clock status updates on your application’s health and error rates. Airbrake-Java easily integrates with all the latest Java frameworks and platforms like Spring , Maven , log4j , Struts , Kotlin , Grails , Groovy , and many more. Plus, Airbrake-Java allows you to easily customize exception parameters and gives you full, configurable filter capabilities so you only gather the errors that matter most.
Check out all the amazing features Airbrake-Java has to offer and see for yourself why so many of the world’s best engineering teams are using Airbrake to revolutionize their exception handling practices!
Ошибка java.lang.nullpointerexception, как исправить?
Ряд пользователей (да и разработчиков) программных продуктов на языке Java могут столкнуться с ошибкой java.lang.nullpointerexception (сокращённо NPE), при возникновении которой запущенная программа прекращает свою работу. Обычно это связано с некорректно написанным телом какой-либо программы на Java, требуя от разработчиков соответствующих действий для исправления проблемы. В этом материале я расскажу, что это за ошибка, какова её специфика, а также поясню, как исправить ошибку java.lang.nullpointerexception.
 Скриншот ошибки NPE
Скриншот ошибки NPE
Что это за ошибка java.lang.nullpointerexception
Появление данной ошибки знаменует собой ситуацию, при которой разработчик программы пытается вызвать метод по нулевой ссылке на объект. В тексте сообщения об ошибке система обычно указывает stack trace и номер строки, в которой возникла ошибка, по которым проблему будет легко отследить.
Что в отношении обычных пользователей, то появление ошибки java.lang.nullpointerexception у вас на ПК сигнализирует, что у вас что-то не так с функционалом пакетом Java на вашем компьютере, или что программа (или онлайн-приложение), работающие на Java, функционируют не совсем корректно. Если у вас возникает проблема, при которой Java апплет не загружен, рекомендую изучить материал по ссылке.
 Ошибка Java
Ошибка Java
Как исправить ошибку java.lang.nullpointerexception
Как избавиться от ошибки java.lang.nullpointerexception? Способы борьбы с проблемой можно разделить на две основные группы – для пользователей и для разработчиков.
Для пользователей
Если вы встретились с данной ошибкой во время запуска (или работы) какой-либо программы (особенно это касается java.lang.nullpointerexception minecraft), то рекомендую выполнить следующее:
- Переустановите пакет Java на своём компьютере. Скачать пакет можно, к примеру, вот отсюда;
- Переустановите саму проблемную программу (или удалите проблемное обновление, если ошибка начала появляться после такового);
- Напишите письмо в техническую поддержку программы (или ресурса) с подробным описанием проблемы и ждите ответа, возможно, разработчики скоро пофиксят баг.
- Также, в случае проблем в работе игры Майнкрафт, некоторым пользователям помогло создание новой учётной записи с административными правами, и запуск игры от её имени.
 Java ошибка в Майнкрафт
Java ошибка в Майнкрафт
Для разработчиков
Разработчикам стоит обратить внимание на следующее:
- Вызывайте методы equals(), а также equalsIgnoreCase() в известной строке литерала, и избегайте вызова данных методов у неизвестного объекта;
- Вместо toString() используйте valueOf() в ситуации, когда результат равнозначен;
- Применяйте null-безопасные библиотеки и методы;
- Старайтесь избегать возвращения null из метода, лучше возвращайте пустую коллекцию;
- Применяйте аннотации @Nullable и @NotNull;
- Не нужно лишней автоупаковки и автораспаковки в создаваемом вами коде, что приводит к созданию ненужных временных объектов;
- Регламентируйте границы на уровне СУБД;
- Правильно объявляйте соглашения о кодировании и выполняйте их.